What Does Skin Cancer Spot On Face Look Like
Medically Reviewed past Debra Jaliman, MD on August 20, 2020

Skin cancers -- including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous prison cell carcinoma -- often start equally changes to your skin. They tin can be new growths or precancerous lesions -- changes that are not cancer but could become cancer over time. An estimated 40% to 50% of blanched people who live to exist 65 will develop at least i peel cancer. Learn to spot the early on warning signs. Skin cancer can be cured if it's found and treated early on.
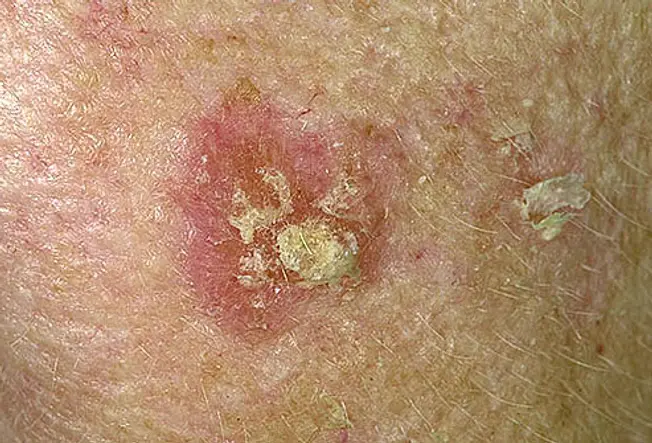
These small, scaly patches are caused by as well much sun, and commonly occur on the caput, cervix, or hands, merely tin be found elsewhere. They can be an early warning sign of skin cancer, simply it's hard to tell whether a detail patch will continue to change over fourth dimension and become malignant. Nearly practice not, but doctors recommend early treatment to preclude the development of squamous cell skin cancer. Off-white-skinned, blond, or ruby-red-haired people with blue or green optics are most at risk.
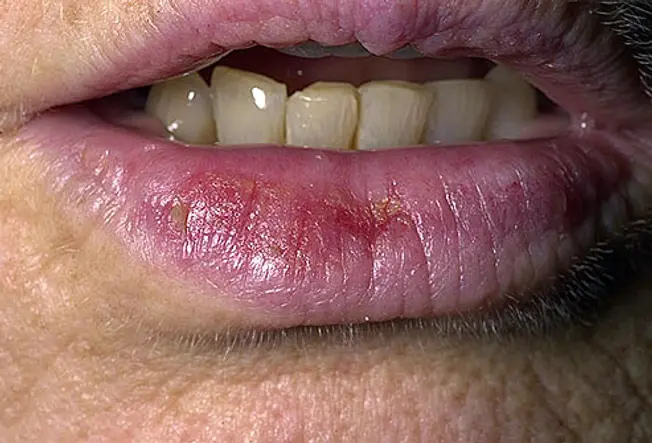
Related to actinic keratosis, actinic cheilitis is a precancerous condition that normally appears on the lower lips. Scaly patches or persistent roughness of the lips may exist present. Less mutual symptoms include swelling of the lip, loss of the sharp edge between the lip and skin, and prominent lip lines. Actinic cheilitis may evolve into invasive squamous cell carcinoma if not treated.
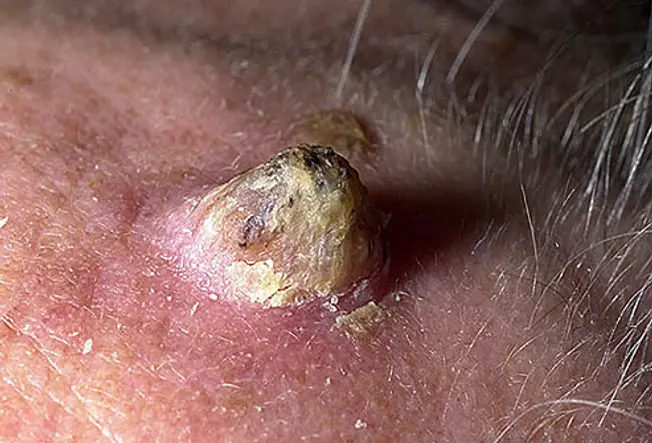
The cutaneous horn appears as a funnel-shaped growth that extends from a red base of operations on the skin. Information technology is composed of compacted keratin (the same poly peptide in nails). It is a specialized type of actininc keratosis. The size and shape of the growth tin vary considerably, but most are a few millimeters in length. Squamous prison cell carcinoma can be found at the base. It usually occurs in fair-skinned elderly adults with a history of significant sun exposure.
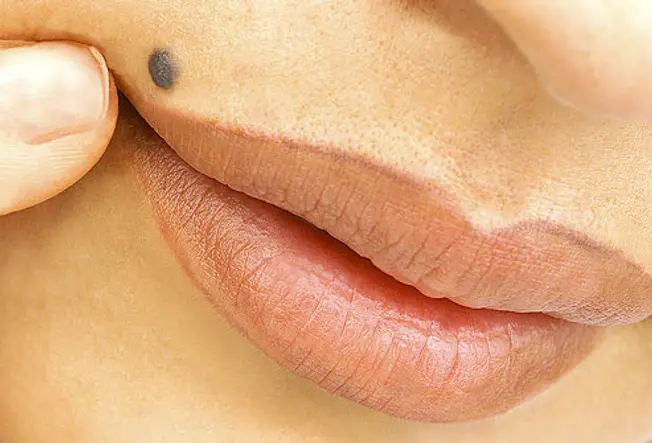
A mole (nevus) is a beneficial growth of melanocytes, cells that gives peel its color. Although very few moles go cancer, abnormal or atypical moles can develop into melanoma over time. "Normal" moles can appear flat or raised or may brainstorm flat and get raised over fourth dimension. The surface is typically smooth. Moles that may accept changed into peel cancer are ofttimes irregularly shaped, contain many colors, and are larger than the size of a pencil eraser. Most moles develop in youth or young adulthood. Information technology's unusual to acquire a mole in the adult years.
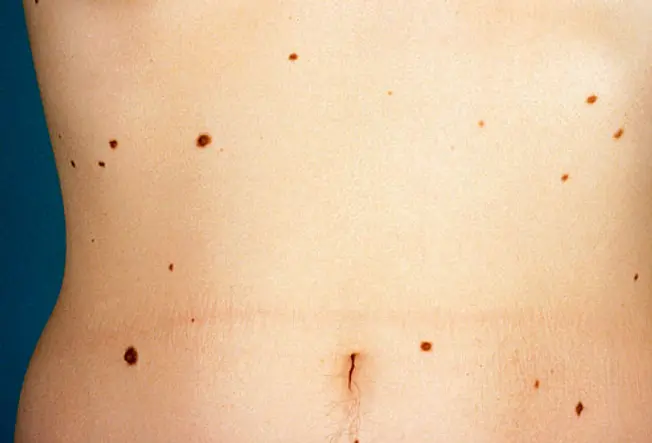
Atypical moles are non cancer, only they can become cancer. They can be plant in dominicus-exposed or lord's day-protected areas of the trunk. Singular moles may be larger (one-quarter inch across or larger) and more irregular in shape, with notched or fading borders. They may exist flat or raised or the surface smooth or rough. They are typically of mixed color, including pink, red, tan, and brown.
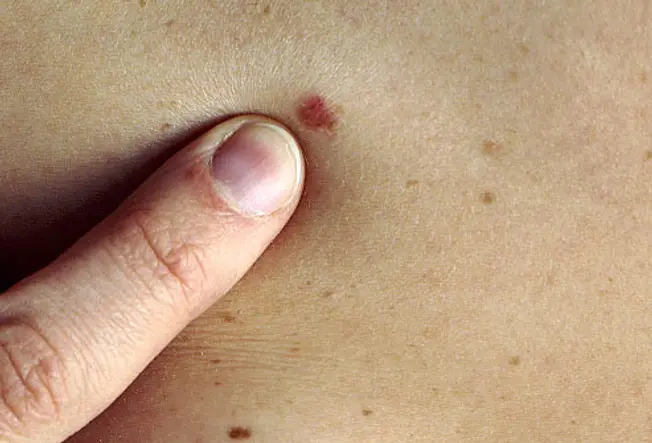
Well-nigh moles on a person'due south body wait similar to ane another. A mole or freckle that looks different from the others or that has any characteristics of the ABCDEs of melanoma should be checked by a dermatologist. It could be cancerous. The ABCDEs are important characteristics to consider when examining your moles or other pare growths, then learn them in the slides to come.
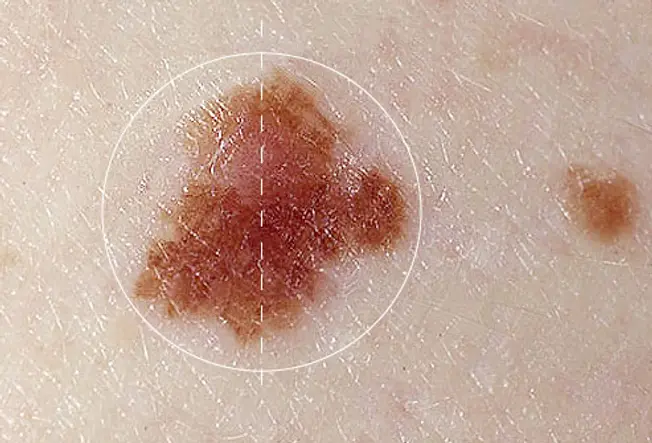
Asymmetry means ane one-half of a mole does not match the other half. Normal moles are symmetrical. When checking your moles or freckles, depict an imaginary line through the heart and compare the two halves. If they do not look the same on both sides, have it checked past a dermatologist.
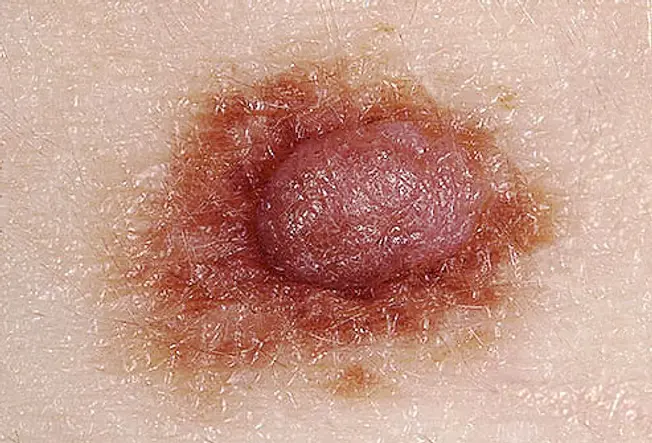
If the border or edges of the mole are ragged, blurred, or irregular, have it checked by a dermatologist. Melanoma lesions oft have uneven borders.
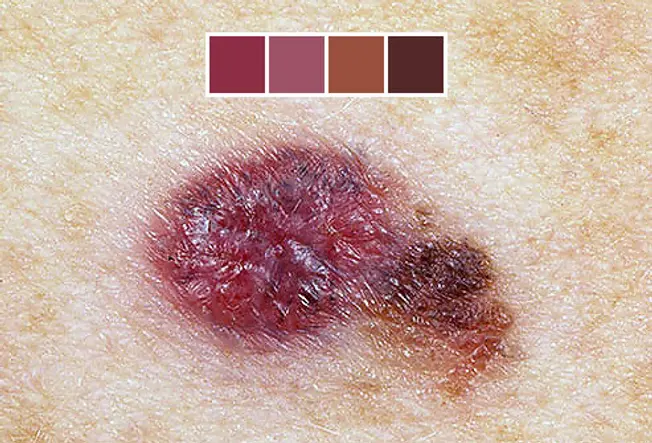
A mole that does not have the same color throughout or that has shades of tan, brown, black, bluish, white, or blood-red is suspicious. Normal moles are usually a single shade of color. A mole of many shades or that has lightened or darkened should be checked by a physician.

A mole is suspicious if the bore is larger than the eraser of a pencil.
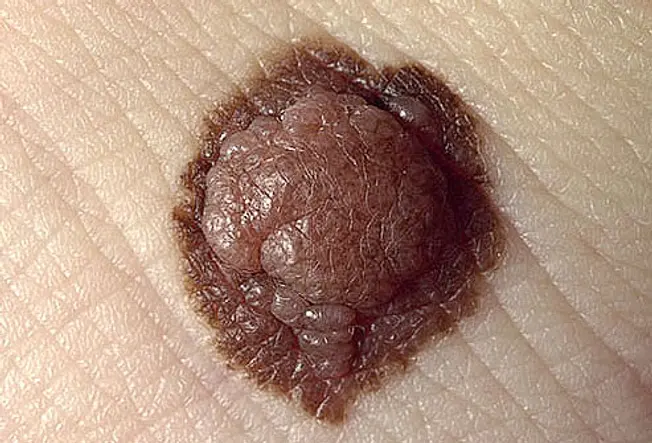
A mole that is evolving – shrinking, growing larger, irresolute color, begins to itch or bleed – should be checked. If a portion of the mole appears newly elevated, or raised from the peel, have it looked at by a doctor. Melanoma lesions often grow in size or alter in height speedily.
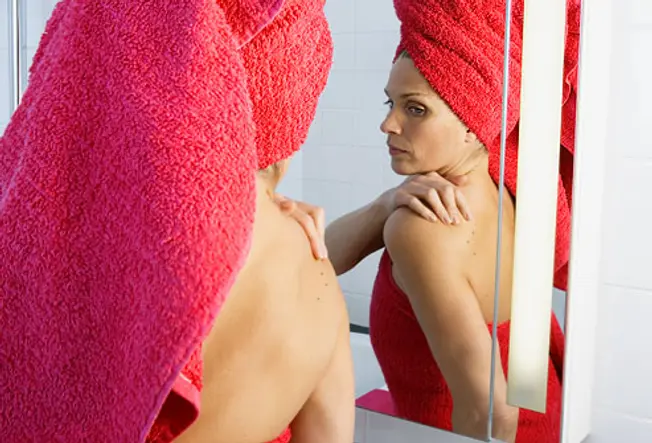

Examine your peel on a regular basis. A common location for melanoma in men is on the back, and in women, the lower leg. Just cheque your entire body for moles or suspicious spots once a month. Start at your caput and piece of work your way down. Check the "hidden" areas: between fingers and toes, the groin, soles of the feet, the backs of the knees. Bank check your scalp and neck for moles. Use a handheld mirror or ask a family unit fellow member to help y'all expect at these areas. Be especially suspicious of a new mole. Take a photograph of moles and appointment information technology to aid yous monitor them for change. Pay special attention to moles if you're a teen, meaning, or going through menopause, times when your hormones may be surging.

If you find a mole or spot that has any ABCDE'south of melanoma -- or one that's tender, itching, oozing, scaly, doesn't heal or has redness or swelling beyond the mole -- see a physician. Your doctor may want to remove a tissue sample from the mole and biopsy it. If institute to be cancerous, the unabridged mole and a rim of normal skin around it will be removed and the wound stitched closed. Additional handling may be needed.
Malignant melanoma, peculiarly in the later stages, is serious and treatment is difficult. Early diagnosis and treatment can increase the survival rate. Nonmelanoma peel cancers include basal cell carcinoma and squamous prison cell carcinoma. Both are common and are about always cured when plant early and treated. People who've had skin cancer once are at risk for getting information technology again; they should become a checkup at least once a twelvemonth.

Melanoma is not as mutual as other types of skin cancer, but information technology's the most serious and potentially deadly. Possible signs of melanoma include a modify in the advent of a mole or pigmented area. Consult a doctor if a mole changes in size, shape, or color, has irregular edges, is more than than one color, is asymmetrical, or itches, oozes, or bleeds.
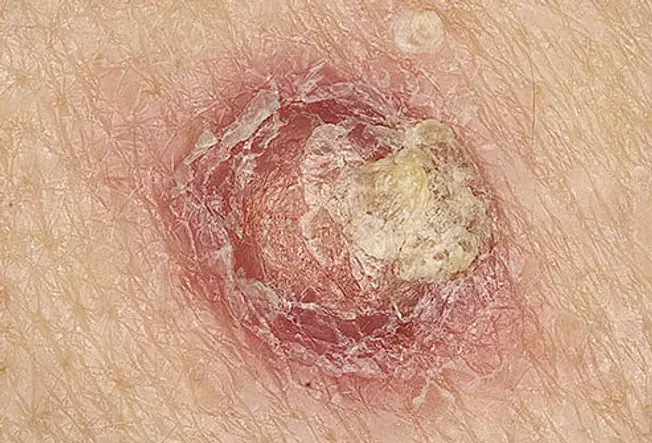
This nonmelanoma skin cancer may appear every bit a firm cherry nodule, a scaly growth that bleeds or develops a crust, or a sore that doesn't heal. Information technology virtually often occurs on the nose, brow, ears, lower lip, hands, and other sun-exposed areas of the trunk. Squamous cell carcinoma is curable if caught and treated early on. If the skin cancer becomes more advanced, treatment will depend on the phase of cancer.
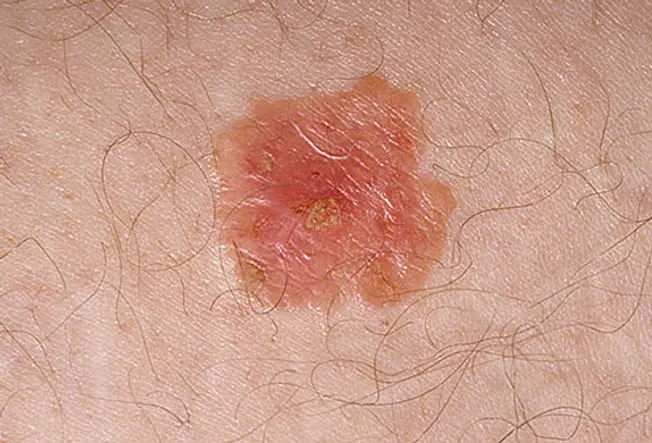
Bowen disease is also called squamous cell carcinoma "in situ." It is a type of skin cancer that spreads outward on the surface of the pare. Past contrast, "invasive" squamous prison cell carcinomas can abound inward and spread to the interior of the body. Bowen affliction looks like scaly, reddish patches that may be crusted; it may be mistaken for rashes, eczema, fungus, or psoriasis.

Basal cell carcinoma is the most common and easiest-to-treat skin cancer. Considering basal cell carcinoma spreads slowly, it occurs more often than not in adults. Basal cell tumors can take on many forms, including a pearly white or waxy bump, oft with visible blood vessels, on the ears, neck, or confront. Tumors can also appear as a apartment, scaly, mankind-colored or brown patch on the dorsum or chest, or more than rarely, a white, waxy scar.

Uncommon types of pare cancer include Kaposi's sarcoma, mainly seen in people with weakened immune systems; sebaceous gland carcinoma, an aggressive cancer originating in the oil glands in the skin; and Merkel cell carcinoma, which is usually institute on sun-exposed areas on the caput, neck, arms, and legs but oft spreads to other parts of the body.

Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn't explain pare cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation handling, and even heredity may play a function. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the run a risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive lord's day exposure or baking sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
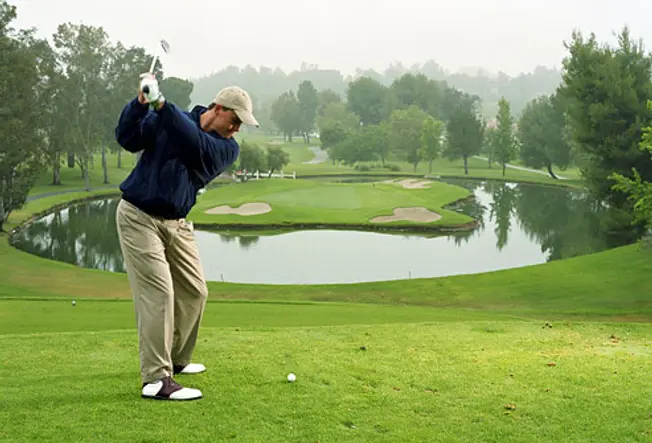

Limit your exposure to the lord's day's ultraviolet rays, especially between x a.m. and iv p.1000., when the sunday'due south rays are strongest. While outdoors, liberally apply a broad spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher (don't forget the lips and ears!), wear a hat and sunglasses, and cover up with vesture. And remember, if you notice changes to your pare such as a new growth, a mole irresolute appearance, or a sore that won't heal, encounter a doctor right mode.
What Does Skin Cancer Spot On Face Look Like,
Source: https://www.webmd.com/melanoma-skin-cancer/ss/skin-cancer-and-skin-lesions-overview
Posted by: lononmarted1980.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Does Skin Cancer Spot On Face Look Like"
Post a Comment